Electrochemically activated Cu2O/Co3O4 nanocomposites on defective carbon nanotubes for the hydrogen evolution reaction†
Abstract
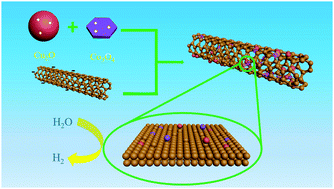
Hydrogen (H2) is an alternative clean and sustainable energy source that could alleviate the fossil fuels crisis, and eco-friendly water electrolysis has been widely employed to produce H2. Herein, we report for the first time the facile synthesis of copper(I) oxide and cobaltosic oxide hybrid nanocomposites decorating defective carbon nanotubes (Cu2O/Co3O4/DC) using a hydrothermal method. Notably, the electrocatalysis of Cu2O/Co3O4/DC is significantly improved through an electrochemical activation process. The electrochemically activated Cu2O/Co3O4/DC (ECA-Cu2O/Co3O4/DC) presents excellent HER activity and durability with a small overpotential of 160 mV at a current density of 10 mA cm−2 and a small Tafel slope of 73 mV dec−1. This high hydrogen evolution performance is attributed to the synergistic interaction between Cu2O/Co3O4 nanoparticles and defective carbon nanotubes, providing further understanding of earth-abundant transition metal-bearing electrocatalysts in emerging energy applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...