Dissimilitude behaviour of Cu2O nano-octahedra and nano-cubes towards photo- and electrocatalytic activities†
Abstract
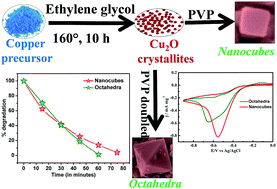
We demonstrate how the morphology of a simple metal-oxide system (e.g., Cu2O) controls catalytic activity. Cu2O catalysts were synthesized with a highly uniform nanocube and nano-octahedra morphology under PVP surfactant-assisted reaction conditions. A series of structural, morphological, optical and electrical characterizations are done to optimize the growth of nanostructures with different morphologies. Finally, the nanostructures are exploited as photo- and electrocatalysts. Interestingly, we find dissimilitude behaviour of nano-octahedra and nano-cube samples towards photo and electrocatalytic activities. The nano-octahedra samples are ∼57% more photocatalytically active (half-life timeoctahedra ∼ 10.7 minutes) than the nanocube samples, which is one of the highest reported photocatalytic efficiencies reported to date. However, the same nano-octahedra samples show lower electrocatalytic activity towards oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) as compared with the nanocube sample.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...