A highly recyclable dip-catalyst produced from palladium nanoparticle-embedded bacterial cellulose and plant fibers
Abstract
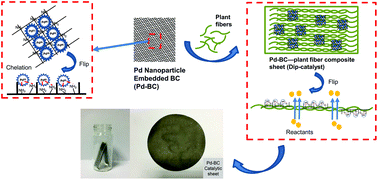
Bacterial cellulose (BC) with its ultrafine nano-reticular structure may provide great support and distribution to metal nanoparticles. In this study, polyethylenimine was introduced into dialdehyde BC to improve the binding stability between BC and palladium (Pd) nanoparticles. The Pd nanoparticle-embedded BC (Pd-BC) was further composited with plant fibers to fabricate a paper-like “dip-catalyst” through a paper handsheet making method. This catalyst has structural features including the fact that PEI-BC provides a great distribution and binding stability to Pd particles, while plant fibers as a supporting component may reduce the cost of fabrication, provide mechanical strength, and improve the contact between the reactants and Pd particles due to their porosity. The dip-catalyst or catalyst sheet was employed in the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction, providing a high reaction rate, a yield of nearly 100% and a high turnover frequency (TOF). It demonstrated an easy reusability and an extensive recycling capability with the same catalyst sheet being used 26 times and still having a yield of nearly 90%. This catalyst sheet produced from sustainable materials is expected to play an important role in organic synthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...