A cobalt catalyst for reductive etherification of 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural to 2,5-bis(methoxymethyl)furan under mild conditions†
Abstract
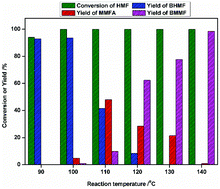
Conversion of platform molecule 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) into high-value-added derivatives has attracted significant interest. In this paper, a metallic cobalt catalyst was prepared by the simple reduction of commercially available Co3O4, and used to catalyze the reductive etherification of HMF to 2,5-bis(methoxymethyl)furan (BMMF) under mild conditions. A yield of 93% 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan (BHMF) was obtained (90 °C, 2 MPa H2, 1 h) and 98.5% yield of BMMF was achieved (140 °C, 2 MPa H2, 1 h) by using a Co-400 catalyst. The catalysts were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), ammonia-temperature-programmed-desorption (NH3-TPD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). It was found that the Co0 and Co2+/3+ species coexist on the surface of the catalyst and the catalyst became more porous and rougher after reduction at high temperature. This may be more beneficial for enhancing the selectivity of the etherification product and the mass transfer of reaction species. A possible reaction mechanism was proposed based on GC and 1H-NMR analyses. The cobalt catalyst was reused five times with a slight decrease in activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...