Enhancing the photostability and bioaccessibility of resveratrol using ovalbumin–carboxymethylcellulose nanocomplexes and nanoparticles†
Abstract
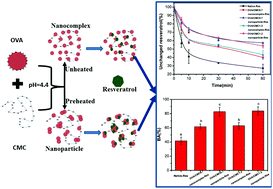
The objective of this study was to investigate the impact of encapsulating resveratrol in ovalbumin (OVA)–carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) nanocomplexes or nanoparticles on its photostability and bioaccessibility. The nanocomplexes were formed by the electrostatic assembly between OVA and CMC, and the nanoparticles were fabricated through further heating the nanocomplexes at 90 °C for 30 min. The nanocomplexes and nanoparticles both presented a spherical morphology, and the nanoparticles exhibited larger average particle sizes and net zeta potential. The encapsulation efficiency and loading capacity were around 26% and 13 μg mg−1 for OVA/CMC nanocomplexes, and evidently increased to around 70% and 35 μg mg−1 for OVA/CMC nanoparticles, respectively. The major driving forces for resveratrol encapsulation were hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction. Both the formulations could improve the photostability of trans-resveratrol when exposed to UV light, and the nanoparticles were more effective. Moreover, the release profile of resveratrol from the nanocapsules in the in vitro simulated gastrointestinal tract was greatly enhanced and could be well fitted using the Higuchi kinetic model and Korsmeyer–Peppas model, indicating a Fickian diffusion release mechanism. Compared to native resveratrol, the bioaccessibility of resveratrol embedded in nanocomplexes and nanoparticles was increased to 60% and 80%, respectively. These findings suggest that OVA/CMC nanocomplexes and nanoparticles have potential applications in the development of effective oral delivery systems of resveratrol as well as other lipophilic nutraceuticals into functional foods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...