Enhanced removal of heavy metals from electroplating wastewater through electrocoagulation using carboxymethyl chitosan as corrosion inhibitor for steel anode†
Abstract
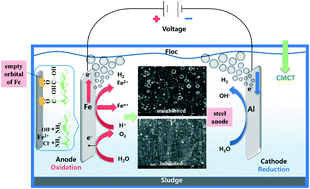
To prolong the life of electrodes, application and evaluation of carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCT), as a corrosion inhibitor for a steel anode, through electrocoagulation during the treatment process of electroplating wastewater was conducted. Among the four tested corrosion candidates, urea, chitosan, dimethylformamide, and carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCT), inhibition efficiency of CMCT for the steel anode was the largest (38.02%). Moreover, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements showed that the charge transfer resistance of CMCT was 502.87 Ω cm−2, compared to 16.82 Ω cm−2 for the control. It was found that under the improved conditions of current density of 35 mA cm−2, initial pH of 3, and CMCT and NaCl concentrations of 75 mg L−1 and 2.5 g L−1 respectively, zinc and nickel ion removal efficiency and inhibition efficiency during the electrocoagulation process reached 93.78%, 30.73% and 36.65%, respectively. Moreover, characterization using XRD and XPS further indicated that the adsorption of CMCT could isolate the steel anode from the solution, thus inhibiting the formation of a passivation layer. Finally, multi-batch experiments confirmed that inhibition efficiency was steady at about 21%. SEM micrographs showed that the surface of steel anode in presence of CMCT exhibits less etched pits than that of the control. Therefore, it is essential to consider the application of CMCT during electrocoagulation process in pilot and even large scale.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...