Antifouling properties of two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide and graphene oxide†
Abstract
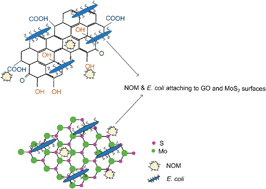
Fouling remains one of the biggest challenges in a myriad of applications such as water filtration, ship hulls, biomedical devices, coating, and painting. Fouling severely hampers the performance and increases the operation and maintenance costs in industries. There is a critical need to develop antifouling surfaces, and two-dimensional (2D) materials, such as graphene oxide (GO) and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), have shown potential for antifouling surface preparation due to some unique properties. Here, the antifouling properties of these two materials were investigated by observing the deposition kinetics of bacteria and natural organic matter (NOM) using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). Suwannee River humic acid (SRHA) and E. coli K-12 were used as model NOM and bacteria, respectively. Overall, MoS2 showed slightly better antifouling properties compared to GO. In most cases, the deposition of NOM and E. coli was significantly lower on MoS2 than GO due to the presence of functional groups on GO that bind more easily with the foulants. Deposition of NOM was at least 1.5 times lower on the MoS2 surface than on the GO surface in the presence of both monovalent (Na+) and divalent (Mg2+) cations. However, the presence of 0.5 mM divalent cations (Ca2+, Mg2+) with NOM reduced the antifouling properties of both MoS2 and GO by a factor of ≥1.5 due to a salt bridging effect and reduced energy barrier.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
