Factors affecting microbial and physico-chemical pollutants in stormwater in a typical Chinese urban catchment
Abstract
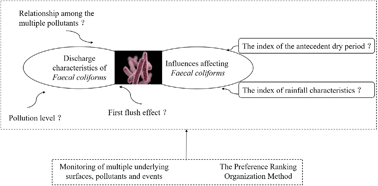
An understanding of microbial pollution characteristics is needed for stormwater reuse and development of microorganism simulations in urban stormwater. This study investigated the discharge characteristics of faecal indicator bacteria (faecal coliforms) in urban runoff by field sampling both the underlying surfaces and the stormwater pipe outlet. Faecal coliform contamination in urban runoff was found to be frequent, and the highest instantaneous concentration reached 2.42 × 106 MPN/100 ml. Faecal coliforms did not show a consistent first flush effect amongst the different surfaces sampled, and this was exacerbated under rainfall events with high intensity. PROMETHEE (Preference Ranking Organization Method for Enrichment Evaluation) and GAIA (Geometrical Analysis for Interactive Aid) analyses were further applied to explore the ranking of pollutants, the relationship among the pollutants, and the factors affecting the contamination in cases of multiple underlying surfaces, multiple pollutants and rainfall events. For the pollutants of suspended solids (SS), total phosphorus (TP) and chemical oxygen demand (COD), the road sample contamination was significantly higher than on the roof surfaces. No such trend in ranking of faecal coliforms was observed. Rainfall depth and intensity were found to have a significant influence on stormwater contamination by physico-chemical pollutants, while having a somewhat smaller influence on faecal coliform contamination. Faecal coliform contamination is closely associated with the index related to the antecedent dry period. The average temperature and average relative humidity also showed a positive relationship with faecal coliform contamination. The effects of antecedent dry period duration on contamination of physico-chemical pollutants and faecal coliform are completely opposite. Antecedent dry period duration was positively related to the contamination of physico-chemical pollutants, but negatively related to faecal coliform contamination. Therefore, three variables, i.e., antecedent dry period duration, average temperature and average relative humidity, might be used to model the survival/die-off of faecal coliform during the antecedent dry period.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...