Implication of iron nitride species to enhance the catalytic activity and stability of carbon nanotubes supported Fe catalysts for carbon-free hydrogen production via low-temperature ammonia decomposition
Abstract
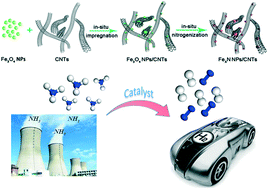
This study was aimed to boost the catalytic ability of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) supported Fe-based catalysts, prepared by using wet-impregnation and followed by nitrogenization, for carbon-free hydrogen production from NH3 decomposition at a low temperature. The nitrogenization temperature and iron loading had significant effects on the size of the well-dispersed Fe2N crystallites. The Fe3O4/CNTs catalysts at a higher nitrogenation temperature under NH3 flow with a suitable Fe content led to the formation of the stable and uniformly distributed Fe2N species, which played an active role in the enhanced catalytic ability of the Fe3O4/CNTs catalysts. However, the nitrogenization of the Fe3O4/CNTs catalyst under either H2 or Ar led to the formation of the Fe4N and Fe2N species. In the presence of the Fe4N phases, the Fe3O4/CNTs catalyst exhibited an enhanced catalytic activity. In brief, the collaborative interaction of the active site Fe2N and carbon nanotubes in the Fe2N/CNTs catalysts resulted in a significant increase in the catalytic activity and durability up to 40 h. The effective control of the density of the active sites Fe2N and the synergism between the carrier and the crystallite composition of iron nitrides are the key aspects for the efficient design of the transition nitride catalysts for carbon-free hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...