Photoelectrocatalytic effect of unbalanced RF magnetron sputtered TiO2 thin film on ITO-coated patterned SiO2 nanocone arrays†
Abstract
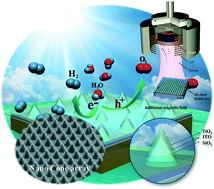
TiO2 has displayed potential for improved catalytic activity using a newly designed morphological system. Herein, a new catalytic system of SiO2/ITO/TiO2 nanocone array structures with unbalanced RF sputtering deposition was developed and demonstrated for photoelectrocatalytic activity. The array structures were fabricated using a soft nanolithography technique with a SiO2 sphere-patterned polydimethylsiloxane stamp. TiO2 films were coated on the ITO-coated SiO2 nanocones using unbalanced RF magnetron sputtering with various external magnetic fields applied by a solenoid. The nanostructures were examined using scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction crystallography, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The photocurrent response in water splitting was found to be increased by 400% for TiO2 films on nano-patterned arrays, compared with that on a flat surface. An additional increase in photocatalytic activity was achieved via TiO2 film deposition with an external magnetic field of 6 mT. This dramatic enhancement was attributed to the surface active sites created by the additional applied magnetic field and the increased surface area of the nanocone arrays.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...