The stability and unexpected chemistry of oxide clusters†
Abstract
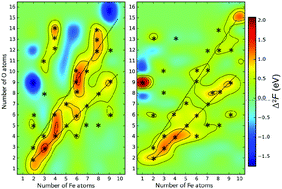
Using evolutionary structure prediction and ab initio thermodynamics, we determine stable compositions and structures of small CemOn and FemOn clusters at realistic temperatures and oxygen pressures. We use second energy differences as the criterion determining clusters of particular stability (“magic” clusters), whereas HOMO–LUMO gaps are used to gauge chemical inertness – i.e. the ability of a cluster to survive in a complex chemical environment. We find that, similar to atomic nuclei (which are clusters made of neutrons and protons), compositional space of two-component clusters also has ridges and islands of stability, surrounded by sea of instability. Long ridges of stability correspond to stoichiometric compositions – e.g., (CeO2)k, (Ce2O3)k, (FeO)k, (Fe2O3)k and (Fe3O4)k series of clusters, while “islands of stability” can have very unexpected compositions. For example, at room temperature and ambient atmosphere, superoxidized Fe4O8 clusters will be dominant among the Fe4On clusters. We emphasize that stability is dictated not only by closed geometric and electronic shells, but also by magnetism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...