Influence of Ce3+ polarons on grain boundary space-charge in proton conducting Y-doped BaCeO3
Abstract
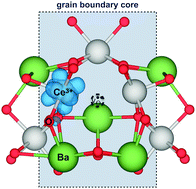
Defect segregation and space-charge formation were investigated for a (0 2 1)[1 0 0] symmetric tilt grain boundary in Y-doped BaCeO3. Density functional theory calculations according to the PBE+U formalism were used to calculate segregation energies for protons, oxygen vacancies and Y-acceptor dopants from the bulk to the grain boundary core. Defect concentration and potential profiles across the grain boundary were obtained from thermodynamic space-charge models. Oxygen vacancies were found to exhibit a particularly exothermic segregation energy of up to −1.66 eV while protons exhibited segregation energies in the range of −0.47 eV to −0.93 eV. The grain boundary was determined to be predominated by protons below 800 K in 3% H2O and the corresponding space-charge potential was 0.4–0.7 V under the Mott–Schottky approximation. The role of electronic defects in the space-charge properties was evaluated, and it was substantiated that electron conduction along the grain boundary could become evident under reducing conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...