Oxygen-reduction catalysis of N-doped carbons prepared via heat treatment of polyaniline at over 1100 °C†
Abstract
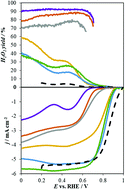
Advanced catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction based on N-doped carbon materials have been designed via pyrolysis of polyaniline at temperatures above 1100 °C. The detailed characterization and computational calculations suggest that the conversion from pyridine to quaternary N in the edge position at high temperatures is responsible for the outstanding activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...