A split aptamer-based imaging solution for the visualization of latent fingerprints†
Abstract
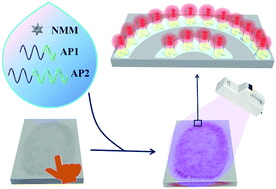
An efficient method for detecting latent fingerprints (LFPs) is very important for personal identification in forensic science. Herein, a simple label-free strategy was designed for the visualization of LFPs by using a split aptamer-based imaging solution. The imaging solution consists of N-methyl mesoporphyrin IX (NMM) molecules and two DNA strands both embedded with split aptamers and split G-quadruplex sequences, respectively. The split aptamers were used to specifically bind with the lysozyme in the residues of LFPs, which brought the two DNA strands into proximity and resulted in the formation of a G-quadruplex/NMM complex. Taking advantage of the high recognition power of the aptamers and the unique fluorescence feature of the G-quadruplex/NMM complex, this split aptamer-based imaging solution was successfully applied for the visualization of LFPs under the irradiation of a handheld UV lamp. Furthermore, this approach was robust for visualizing LFPs on different substrates and from different volunteers. Therefore, this LFP imaging strategy might find wide application in forensic investigations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...