Facile regrowth of Mg-Fe2O3/P-Fe2O3 homojunction photoelectrode for efficient solar water oxidation†
Abstract
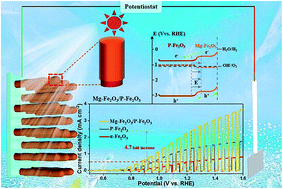
The photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting performance of hematite-based photoanodes is still far from their theoretical value due to the ultrafast charge recombination in bulk and on the surface. In response, we developed a regrowth strategy to fabricate a photoanode with metallic Mg-doped α-Fe2O3 coating on nonmetallic P-doped α-Fe2O3 nanorods (Mg-Fe2O3/P-Fe2O3 NRs). This homojunction structure fulfils the requirements of both high charge separation efficiency and favorable band alignment, showing a high photocurrent density (4.7-fold higher than pristine Fe2O3) and low onset potential of 0.68 VRHE. Experimental and density functional theory (DFT) results reveal that the origin of such superior PEC performance is P-doping and Mg-Fe2O3 coating, which efficiently eliminate lattice mismatching, improve the conductivity of hematite, and simultaneously promote the photogenic carriers separation by the built-in electric field. This promising design may open an avenue to fabricating various efficient homojunction photoanodes for practical PEC water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...