Microfluidic capacitive sensors with ionic liquid electrodes and CNT/PDMS nanocomposites for simultaneous sensing of pressure and temperature†
Abstract
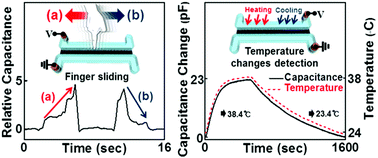
We report a new class of simple fluidic capacitive sensors based on microfluidic techniques, which are capable of multimodal sensing performances. The microfluidic multifunctional capacitive sensors were realized by using ionic liquids acting as electrodes in microchannels and a CNT/PDMS composite as a dielectric layer. Our microfluidic capacitive sensors offer outstanding sensor performance to detect localized pressure and even lateral pressure variation as well as ambient temperature changes. The principle of our new microfluidic capacitive sensors is explained by the electric double layer capacitance and the ion distribution along the ionic liquid electrodes. In order to demonstrate their capability for practical usage, our simple structured microfluidic capacitive sensors were applied to a bottle and human skin for monitoring the variation of pressure and temperature simultaneously. The highly sensitive microfluidic capacitive sensors were successfully applied as keypads and potential platforms for distinctively detecting various hand or finger motions such as tapping, scratching, and stacking. Our novel microfluidic multimodal capacitive sensors show great promise for making future stretchable electronic devices, such as wearable electronics, soft robotics, and artificial skin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...