Synthesis of silver-anchored polyaniline–chitosan magnetic nanocomposite: a smart system for catalysis
Abstract
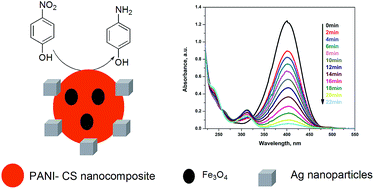
A simple route was employed for the fabrication of a polyaniline (PANI)–chitosan (CS)–magnetite (Fe3O4) nanocomposite (PANI–CS–Fe3O4) via the in situ polymerization of aniline in the presence of CS using anhydrous iron(III) chloride as an oxidizing agent. The magnetic character of the nanocomposite results from the presence of iron oxide nanoparticles, which were formed as side products during the synthesis of the PANI–CS nanocomposite. The synthesized PANI–CS–Fe3O4 nanocomposite was fully characterized using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM). The reduction of silver nitrate by the synthesized nanocomposite enables the anchoring of silver (Ag) nanoparticles onto its surface. The catalytic properties of the Ag-decorated nanocomposite (Ag@PANI–CS–Fe3O4) toward the reduction of 4-nitrophenol was investigated using sodium borohydride as a reducing agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...