High-quality cadmium stannate annealed in N2 atmosphere for low-cost thin film solar cell†
Abstract
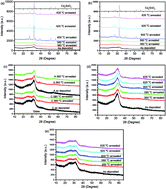
Radio frequency magnetron sputtered cadmium stannate (Cd2SnO4) or cadmium tin oxide (CTO) films were annealed in a nitrogen (N2) atmosphere. The resistivity of argon/oxygen (Ar/O2) gas sputtered CTO films decreased drastically after high temperature annealing, and the lowest resistivity of 1.73 × 10−4 Ω cm was achieved. The Cd2SnO4 crystal phase of CTO films deposited in Ar/O2 gas occurred after annealing at 600 °C to 635 °C, and the optical band gap increased obviously after annealing. When the deposition atmosphere was pure Ar, the as-deposited CTO resistivity was in the order of 10−4 Ω cm. The resistivity of thin films deposited in Ar gas could decline slightly after annealing. However, the resistivity of thick films deposited under Ar gas increased drastically after annealing. No Cd2SnO4 crystal phase of Ar gas sputtered CTO occurred after annealing. The visible region and near infrared spectrum transmittance of CTO films increased after annealing in a N2 atmosphere. The resistivity of CTO films deposited in Ar/O2 and after annealing in N2 gas at 620 °C increased slightly after chlorine treatment. Furthermore, the resistivity of films deposited in Ar/O2 and then annealed in N2 gas at 620 °C decreased slightly after vacuum annealing at 600 °C for 5 min.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...