An enzymatic strategy to asymmetrically branched N-glycans†
Abstract
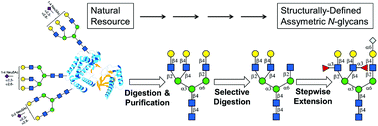
An enzymatic strategy was developed to generate asymmetrically branched N-glycans from natural sources by using a panel of glycosidases and glycosyltransferases. Briefly, LacZ β-galactosidase was employed to selectively trim symmetrically branched N-glycans isolated from bovine fetuin. The yielding structures were then converted to asymmetrically branched core structures by robust glycosyltransferase for further extension.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...