β-O-4 type dilignol compounds and their iron complexes for modeling of iron binding to humic acids: synthesis, characterization, electrochemical studies and algal growth experiments†
Abstract
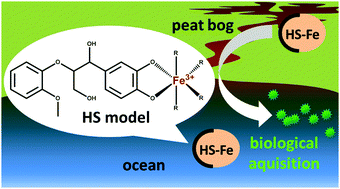
A series of β-O-4 type dilignols and their iron(III) complexes, designed as model compounds for humic acids, were prepared and characterized by 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, EPR, IR and UV-Vis spectroscopies and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). Properties regarding iron binding, stability, lipophilicity and bioavailability for microorganisms have been evaluated with cyclic voltammetry, stability studies in water and seawater by means of UV-Vis spectrophotometry and the algae growth assays with seawater algal species Chlorella salina and Prymnesium parvum. Both established ligands and their iron complexes undergo deprotonation processes in seawater whereas no changes in UV-Vis spectra were observed in distilled water. The iron(III) complex formation constants, pKa values and lipophilicity of the dilignols were in the same range as for the analogous catechol coordination compound. Synthesized dilignols were prone to redox reactions under biological conditions similar to natural aquatic humic acids. Moreover, an increased iron bioavailability was observed for the presented complexes compared to corresponding catechol complexes and comparable to the bioavailability of iron bound to humic acid complexes recovered from Craggie Burn river. Those results confirm that β-O-4 type dilignol compounds are excellent model ligands for aquatic humic acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...