Anchoring di and tri-metallic nanoparticles on an amorphous functionalized surface for inducing photocatalytic activity†
Abstract
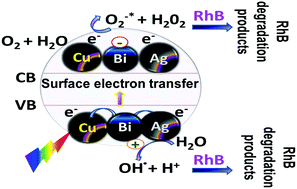
This study aimed at establishing a method for developing a new type of photocatalyst that can interact with visible light to become suitable for taking advantage of visible sunlight that accounts for more than 95% of the sunlight falling on the earth. This was successfully achieved by producing di and tri metal nanoparticles chemically attached to a functionalized amorphous surface, using two different functional groups. This study reports for the first time a very efficient and economical chemical synthesis process for the preparation of well-distributed di- and tri-metallic nanoparticles (Ag–Au, Au–Cu, and Ag–Bi–Cu) chemically decorated on amorphous silica, amine-modified silica (AFS), and mercapto-modified silica (MFS) supports for enhancing the photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB). The structural and optical properties of the prepared materials and their catalytic efficiency were examined using multiple characterization analysis techniques. TEM micrographs show 5 to 10 nm metal nanoparticles uniformly distributed on the amorphous silica support. The UV-Vis absorbance analysis shows a considerable plasmonic shift between the samples before and after reduction. These (green) innovative catalysts have superior activity in visible light and offer many advantages such as affordability, recyclability, and ability to work under ambient conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...