A novel (3,6-di-tert-butylcarbazol-9-yl) triphenylamine–BODIPY–tricyanofuran conjugated dye: synthesis and rapid naked-eye detection of hypochlorite†
Abstract
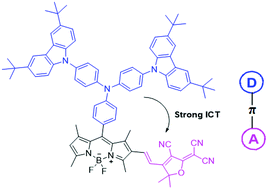
Herein, a colorimetric and ratiometric probe, BCPA–BODIPY–TCF, for hypochlorite (ClO−) based on a D–π–A structure was synthesized through the Knoevenagel reaction, which consisted of donating groups (3,6-di-tert-butylcarbazol-9-yl)triphenylamine–BODIPY conjugated with a strong electronic acceptor group, 2-dicyanomethylene-4,5,5-trimethyl-3-cyano-2,5-dihydrofuran (tricyanofuran). Upon the addition of ClO−, the probe displayed rapid identification, immediately accompanied with color change from purple to pink in one minute; this was attributed to the oxidative cleavage of an alkene linker between BODIPY and tricyanofuran. The introduction of tricyanofuran at the 2-position of BODIPY through a C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond made the absorption peak red-shift by 85 nm as compared to that of the precursor BCPA–BODIPY due to a strong intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) transition. Upon the addition of ClO−, the absorption peak at 580 nm gradually decreased, and the absorption band centred at 500 nm concomitantly increased. The probe was highly selective for ClO− detection without the interference of other anions and ROS. Additionally, a paper-based test strip was prepared and used as a naked-eye indicator for the presence of hypochlorite in practical tap water samples.
C double bond made the absorption peak red-shift by 85 nm as compared to that of the precursor BCPA–BODIPY due to a strong intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) transition. Upon the addition of ClO−, the absorption peak at 580 nm gradually decreased, and the absorption band centred at 500 nm concomitantly increased. The probe was highly selective for ClO− detection without the interference of other anions and ROS. Additionally, a paper-based test strip was prepared and used as a naked-eye indicator for the presence of hypochlorite in practical tap water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...