Synthesis of an electronically conductive hydrogel from a hydrogelator and a conducting polymer†
Abstract
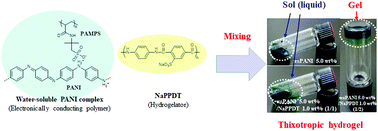
The present study demonstrates that the synthetic output of a polymer hydrogelator and a water-soluble electronically conductive polymer exhibits thixotropy due to the hydrogelator although each component at low concentrations does not exhibit this behaviour. The composite hydrogel exhibits semiconducting electronic conductivity and is insoluble in aqueous electrolyte solutions. These properties constitute significant advantages for applications in polymer electrodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...