Green primary energetic materials based on N-(3-nitro-1-(trinitromethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)nitramide†
Abstract
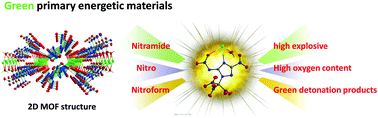
In this study, a series of high-energy-density materials (1·2H2O–9) based on N-(3-nitro-1-(trinitromethyl)-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)nitramide were synthesized and structurally characterized using 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The crystal results demonstrated that potassium 3-nitro-5-(nitroimino)-1-(trinitromethyl)-1,2,4-triazolate hydrate (2·H2O) exhibits an infinite two-dimensional (2D) metal–organic framework (MOF) containing the coordination group NO2 and metal cation K+. Additionally, this 2D MOF exhibited a high oxygen content (46.41%) and a positive oxygen balance (14.77%). Heats of formation and the detonation properties of the newly prepared compounds were calculated using the Gaussian 09 and EXPLO 5 programs, respectively. Energetic evaluation indicated that these compounds demonstrate good detonation performances, all of which outperform traditional primary explosives mercury fulminate, lead azide, 2-diazo-4,6-dinitrophenol, and in some cases, even exceed the performance of high explosive RDX. Therefore, the high detonation parameters of the compounds enable these potential primary explosives to trigger the whole detonation easily. Furthermore, several attractive properties, such as an excellent density (2.00 g cm−3), an impact sensitivity of 2 J, a friction sensitivity of 32 N, and a low amount of toxic detonation products, make 2·H2O an eco-friendly primary explosive.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...