Supramolecular combinations of humic polyanions as potent microbicides with polymodal anti-HIV-activities†
Abstract
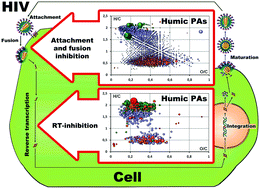
This article focuses on linking structures of fractionated humic polyanions (PAs), which were molecularly defined using ultrahigh resolution Fourier transform mass spectrometry (FTMS), to their antiviral activities with respect to laboratory HIV-1 strains. Anti-HIV-1 activity was proven using a full HIV-1 replication system validated for antiviral testing. We demonstrated that all humic PAs tested in our study were capable of inhibiting HIV fusion. The most hydrophobic fractions of humic and hymatomelanic PAs also strongly inhibited HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. The structure–activity analysis revealed the direct relationship of antiviral activities with contribution of CHO molecules in humic PA composition and lipophilicity index, and the inverse relationship with their carboxylic and total acidity. This was explained by the supramolecular character of humic PAs, the properties of which are ruled rather by the contribution of most potent scaffolds than by the total charge density. It is concluded that all humic PAs tested in this study can be considered as promising precursors for developing cost-effective combinatorial microbicides with polymodal anti-HIV activity and low cytotoxicity capable of preventing HIV-1 transmission.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...