N-tert-Prenylation of the indole ring improves the cytotoxicity of a short antagonist G analogue against small cell lung cancer†‡
Abstract
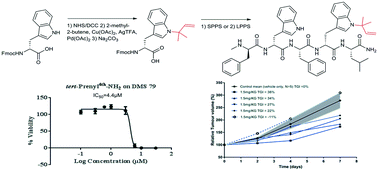
Natural prenylated indoles have been proposed as potential anticancer agents. To exploit this discovery for developing new peptide therapeutics, we report the first studies whereby incorporation of prenylated indoles into primary sequences has been achieved. We developed a route to synthesise Nα-Fmoc-protected tryptophan derivatives in which the prenyl group is linked to the N-indole core, using Pd(II)-mediated C–H functionalisation of 2-methyl-2-butene. Based on the Substance P antagonist G (SPG), a well-known Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) anticancer agent, we designed a new penta-peptide sequence to include a prenyl moiety on one of the tryptophan residues. The N-tert-prenylated tryptophan analogue was assembled into the pentameric peptide using standard solid phase peptide synthesis or liquid phase synthesis by fragment coupling. In vitro screening showed that the N-tert-prenylation of the indole ring on the tryptophan residue located near the C-terminal of the penta-peptide enhanced the cytotoxicity against H69 (IC50 = 2.84 ± 0.14 μM) and DMS79 (IC50 = 4.37 ± 0.44 μM) SCLC cell lines when compared with the unmodified penta-peptide (H69, IC50 = 30.74 ± 0.30 μM and DMS79, IC50 = 23.00 ± 2.07 μM) or the parent SPG sequence (IC50 > 30 μM, both cell lines). SCLC almost invariably relapses with therapy-resistant disease. The DMS79 cell line was established from a patient following treatment with a number of chemotherapeutics (cytoxan, vincristine and methotrexate) and radiation therapy. Treating DMS79 tumour-bearing nude mice provided a human xenograft model of drug resistance to test the efficacy of the prenylated peptide. A low dose (1.5 mg kg−1) of the prenylated peptide was found to reduce tumour growth by ∼30% (P < 0.05) at day 7, relative to the control group receiving vehicle only. We conclude that the availability of the Fmoc-Trp(N-tert-prenyl)-OH amino acid facilitates the synthesis of prenylated-tryptophan-containing peptides to explore their therapeutic potential.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...