Design, synthesis, molecular-docking and antimycobacterial evaluation of some novel 1,2,3-triazolyl xanthenones†‡
Abstract
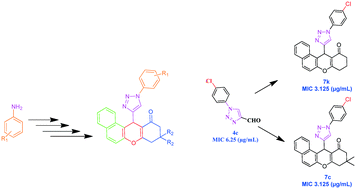
As part of an ongoing effort to develop new antitubercular and antimicrobial agents, a series of substituted xanthenone derivatives (7a–p) were synthesized. Xanthenone derivatives (7a–p) were prepared via a one-pot three-component thermal cyclization reaction of β-naphthol (5), substituted 1-aryl-1H-[1,2,3]triazole-4-carbaldehydes (4a–h), and cyclic-1,3-diones (6a, b) in the presence of a catalytic amount of iodine. The newly synthesized compounds were characterized by IR, NMR, mass spectral data, and elemental analysis. These compounds (4a–h and 7a–p) were screened for in vitro antitubercular activity against the M. tuberculosis H37Rv (ATCC 27294) strain, for antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains, and for antifungal activity against a pathogenic strain of fungi. Among the compounds tested, most of them showed good to excellent antimicrobial and antitubercular activity. The active compounds displaying good potency in the MTB were further examined for toxicity in a HEK cell line. In addition, the structure and antitubercular activity relationship were further supported by in silico molecular-docking studies of the active compounds against the pantothenate synthetase (PS) enzyme of M. tuberculosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...