Structural features of many circular and leaderless bacteriocins are similar to those in saposins and saposin-like peptides†‡
Abstract
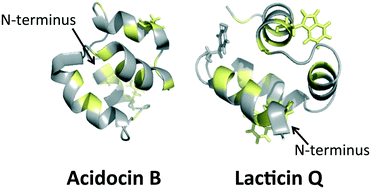
Bacteriocins are potent antimicrobial peptides that are ribosomally produced and exported by bacteria, presumably to aid elimination of competing microorganisms. Many circular and linear leaderless bacteriocins have a recuring three dimensional structural motif known as a saposin-like fold. Although these bacteriocin sizes and sequences are often quite different, and their mechanisms of action vary, this conserved motif of multiple helices appears critical for activity and may enable peptide–lipid and peptide–receptor interactions in target bacterial cell membranes. Comparisons between electrostatic surfaces and hydrophobic surface maps of different bacteriocins are discussed emphasizing similarities and differences in the context of proposed modes of action.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...