Targeting Twist expression with small molecules†
Abstract
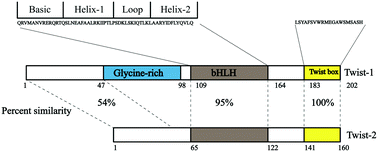
Twist, as one of the important embryonic transcription factors, regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and migration in embryo formation and cancer development. Both Twist-1 and Twist-2 are rarely detectable in healthy adult tissues, but are frequently overexpressed in multiple kinds of human cancer tissues, such as breast, prostate, uterus, liver, melanoma, etc. Twist is considered as a crucial EMT inductor and correlated with carcinoma aggression, invasion and metastasis. In the past decades, in-depth investigation has been reported in terms of the role of Twist in cancers; in addition, several kinds of small molecules have played important roles in studying the effect of Twist on cancer development, suggesting that Twist can be regarded as one of the important potential targets for cancer treatment. Hence we provide a brief overview of Twist and several small molecules targeting its expression, highlighting the biological features that make it a charming target for cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...