A biomaterial screening approach reveals microenvironmental mechanisms of drug resistance†
Abstract
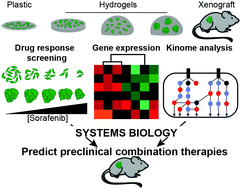
Traditional drug screening methods lack features of the tumor microenvironment that contribute to resistance. Most studies examine cell response in a single biomaterial platform in depth, leaving a gap in understanding how extracellular signals such as stiffness, dimensionality, and cell–cell contacts act independently or are integrated within a cell to affect either drug sensitivity or resistance. This is critically important, as adaptive resistance is mediated, at least in part, by the extracellular matrix (ECM) of the tumor microenvironment. We developed an approach to screen drug responses in cells cultured on 2D and in 3D biomaterial environments to explore how key features of ECM mediate drug response. This approach uncovered that cells on 2D hydrogels and spheroids encapsulated in 3D hydrogels were less responsive to receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-targeting drugs sorafenib and lapatinib, but not cytotoxic drugs, compared to single cells in hydrogels and cells on plastic. We found that transcriptomic differences between these in vitro models and tumor xenografts did not reveal mechanisms of ECM-mediated resistance to sorafenib. However, a systems biology analysis of phospho-kinome data uncovered that variation in MEK phosphorylation was associated with RTK-targeted drug resistance. Using sorafenib as a model drug, we found that co-administration with a MEK inhibitor decreased ECM-mediated resistance in vitro and reduced in vivo tumor burden compared to sorafenib alone. In sum, we provide a novel strategy for identifying and overcoming ECM-mediated resistance mechanisms by performing drug screening, phospho-kinome analysis, and systems biology across multiple biomaterial environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...