Catalyst-free aerobic oxidation of aldehydes into acids in water under mild conditions†
Abstract
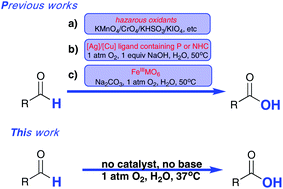
The first example of catalyst-free aerobic oxidation of aldehydes in water under respective acidic, neutral and alkaline conditions was developed. The sole oxidant is molecular oxygen of 1 atmosphere and reactions can proceed under extremely mild conditions. This procedure covers a wide range of aldehydes, and operates easily. No additives and catalysts were required for this purpose, and most of the aldehydes can be converted to their corresponding carboxylic acids with good to excellent yields, in addition, no side-product formation could be observed during or after the reactions. To well illustrate why the oxidation rate becomes fast firstly and then slows with increased temperatures, five control reactions were carried out and a Fe3+/Fe2+ recycling system was introduced to facilitate the aldehyde oxidation rate. The generality of this method offers the potential for industrial aldehyde-containing waste water treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...