Highly effective C–C bond cleavage of lignin model compounds†
Abstract
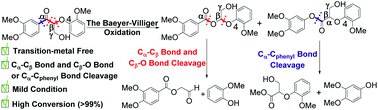
A highly effective method is developed for the C–C bond cleavage of lignin model compounds. The inert Cα–Cβ or Cα–Cphenyl bond of oxidized lignin model compounds was successfully converted to an active ester bond through the classic organic name reaction, Baeyer–Villiger (BV) oxidation, and thus acetal esters and aryl esters were produced in high yields (up to 99%) at room temperature. Next, K2CO3 catalyzed the alcoholysis of the resulting ester products at 45 °C, affording various useful chemical platforms in excellent yields (up to 99%), such as phenols and multifunctional esters. This method uses commercially available reagents, is transition-metal free and simple, but highly effective, and involves mild reaction conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...