Balancing gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen density in MOFs†
Abstract
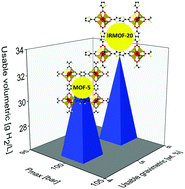
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising materials for the storage of hydrogen fuel due to their high surface areas, tunable properties, and reversible gas adsorption. Although several MOFs are known to exhibit high hydrogen densities on a gravimetric basis, realizing high volumetric capacities – a critical attribute for maximizing the driving range of fuel cell vehicles – remains a challenge. Here, MOFs that achieve high gravimetric and volumetric H2 densities simultaneously are identified computationally, and demonstrated experimentally. The hydrogen capacities of 5309 MOFs drawn from databases of known compounds were predicted using empirical (Chahine rule) correlations and direct atomistic simulations. A critical assessment of correlations between these methods, and with experimental data, identified pseudo-Feynman–Hibbs-based grand canonical Monte Carlo calculations as the most accurate predictive method. Based on these predictions, promising MOF candidates were synthesized and evaluated with respect to their usable H2 capacities. Several MOFs predicted to exhibit high capacities displayed low surface areas upon activation, highlighting the need to understand the factors that control stability. Consistent with the computational predictions, IRMOF-20 was experimentally demonstrated to exhibit an uncommon combination of high usable volumetric and gravimetric capacities. Importantly, the measured capacities exceed those of the benchmark compound MOF-5, the record-holder for combined volumetric/gravimetric performance. Our study illustrates the value of computational screening in pinpointing materials that optimize overall storage performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...