Highly thermally stable and robust enantiopure zirconium NNN-scorpionates for the controlled ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide†
Abstract
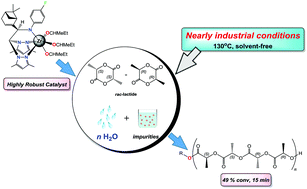
A series of enantiopure alkoxide and thioalkoxide zirconium derivatives [Zr(ER)3(κ3-R,R-fbpza)] (1–6) (E = O, R = CHMe21, CHMeEt 2, CH2SiMe33, 2,6-C6H3Me24, 4-tBuPh 5; E = S, R = 4-tBuPh 6) has been prepared for use as thermally stable and robust initiators in the ROP of rac-lactide. The compounds were prepared by alcoholysis or thioalcoholysis of the tris(amide) precursor [Zr(NMe2)3(κ3-R,R-fbpza)] [R,R-fbpzaH = N-p-fluorophenyl-(1R)-1-[(1R)-6,6-dimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]-2-hepten-2-yl]-2,2-bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)ethylamine] with ROH and ArEH (E = O, S) in a 1 : 3 molar ratio. The structures of the different compounds were determined by spectroscopic methods and, in addition, the X-ray crystal structure of 6 was also established. Interestingly, the tris(amide) precursor and complexes 2, 5, and 6 act as single-site living initiators for the well-controlled ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide both in solution and in the melt. These processes produce polymers with medium molecular weights in good agreement with theoretical values and with narrow dispersity ranges. The activity of all initiators increased markedly with temperature and, more importantly, complex 2 exhibits the highest activity reported to date for a group 4-based initiator in the ROP of rac-LA under the industrially preferred melt and solvent-free conditions. Surprisingly, complex 2 is still highly active in the melt when using an unpurified monomer and it shows an unprecedented tolerance to water and impurities (49% conv., 15 min, 130 °C). Microstructural analysis of the poly(rac-lactide)s revealed a moderate heteroactivity in solution, with a Ps value of up to 0.70.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...