Manganese-containing ionic liquids: synthesis, crystal structures and electrodeposition of manganese films and nanoparticles†
Abstract
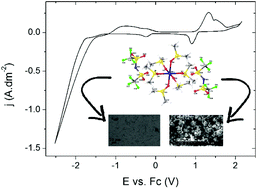
Manganese(II)-containing ionic liquids were synthesized, in which the manganese atoms are coordinated by glymes (diglyme, triglyme, tetraglyme), pyridine-N-oxide, dimethylsulfoxide or N-alkylimidazoles (N-methylimidazole, N-butylimidazole and N-hexylimidazole). As anion, bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (bistriflimide, Tf2N−), trifluoromethanesulfonate (triflate, OTf−) or methanesulfonate (mesylate, OMs−) were used. The compounds were characterized by CHN analysis, FTIR, DSC and single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurements. All manganese atoms were six-coordinate. It was found that the glyme-type ligands were replaced by atmospheric water upon leaving the crystals open to the air for several days. The crystal structures of seven compounds were described in detail and the compounds with the lowest melting temperatures were tested as electrolytes for the electrodeposition of manganese (thin) films. An irreversible reduction wave from Mn(II) to Mn(0) and granular manganese deposits were observed for all compounds, except for liquid manganese salts with N-alkylimidazole ligands and bistriflimide anions, where the electrochemical formation of manganese nanoparticles was observed instead of the deposition of a manganese layer. However, for compounds with the same cation but with a triflate or methanesulfonate anion, manganese metal deposits were obtained, indicating that the nature of the anion has an important effect on the electrochemical properties of liquid metal salts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...