Trivalent f-elements in human saliva: a comprehensive speciation study by time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy and thermodynamic calculations†
Abstract
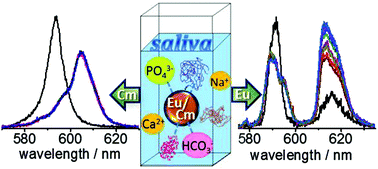
In the case of oral ingestion of radioactive contaminants, the first contact medium is saliva in the mouth. To gain a first insight into the interaction of radioactive contaminants in human saliva, the speciation of curium (Cm(III)) and europium (Eu(III)), i.e., trivalent f-elements, was investigated in different salivary media with time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The results indicate that these metal cations are primarily complexed with carbonates and phosphates, forming ternary complexes with a possible stoichiometry of 1 : 1 : 2 (M(III) : carbonate : phosphate). For charge compensation, calcium is also involved in these ternary complexes. In addition to these inorganic components, organic substances, namely α-amylase, show a significant contribution to the speciation of the trivalent f-elements in saliva. This protein is the major enzyme in saliva and catalyzes the hydrolysis of polysaccharides. In this context, the effect of Eu(III) on the activity of α-amylase was investigated to reveal the potential implication of these metal cations for the in vivo functions of saliva. The results indicate that the enzyme activity is strongly inhibited by the presence of Eu(III), which is suppressed by an excess of calcium.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...