Probing promoting effects of alkali cations on the reduction of CO at the aqueous electrolyte/copper interface†
Abstract
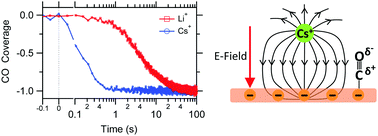
The catalytic selectivity and reactivity of an electrocatalytic interface can profoundly depend on the identity of the supporting electrolyte's cation. In the case of CO2 reduction on copper electrodes, these cation effects have been utilized to suppress undesired hydrogen evolution and to promote the formation of C2 reduction products. However, to more effectively steer the catalytic selectivity of the electrolyte/copper interface by cations, it is crucial to reveal the various physical mechanisms by which cations impact the catalytic properties of this prototypical interface for CO2 reduction. Herein, we employ surface-sensitive infrared spectroscopy to probe how alkali cations (Li+, K+, and Cs+) control the coverage of CO, a key intermediate in CO2 reduction, on a polycrystalline copper electrode. We find that surface-adsorbed CO experiences an increasingly larger interfacial electric field with increasing cation size. The reduction of CO is further promoted by the two larger cations, leading to a significant drop of the CO coverage at high cathodic potential around −1 V vs. RHE. Our results demonstrate for the first time that the coverage of CO on the electrode is very sensitive to the identity of the cation. Since the relative coverage of CO and hydrogen on the copper surface affects the catalytic rates of CO2 reduction and hydrogen evolution, our results represent an essential step towards a better understanding of how cation effects control the product distribution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...