Proposal of a new mechanism for the directional propagation of the action potential using a mimicking system†
Abstract
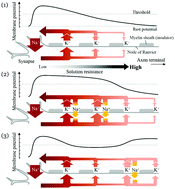
A nerve conduction model is constructed by using some liquid-membrane cells that mimic the function of the K+ and Na+ channels. By imitating two types of Na+ channels (ligand-gated Na+ channels and voltage-gated Na+ channels), a new mechanism for the directional propagation of the action potential along the axon toward the axon terminal is proposed. When the nerve cell is excited by an external (outer) stimulus, it can be presumed that the ligand-gated channels work as power sources at the synapse to propagate the change in the membrane potential, and then the voltage-gated channels locally assist the propagation at each site of the axon (nodes of Ranvier).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...