A sensitive immunosensor for microcystin-(leucine–arginine) based on fluorescent self-assembled multilayers
Abstract
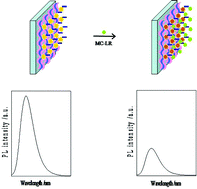
In this paper, a novel fluorescent immunosensor based on self-assembled multilayers was constructed to detect microcystin-(leucine–arginine). CdTe quantum dots were firstly assembled on the quartz substrates. Then bioconjugates were formed by an amidation reaction between CdTe quantum dots and microcystin-(leucine–arginine) antibodies. The sensing system exhibited a linear range from 0.0001 to 3 μg L−1 for microcystin-(leucine–arginine) with a detection limit of 0.0440 ng L−1, 2–4 orders of magnitude lower than most other fluoroimmunoassays. Desirable results were also obtained in natural lake water and interference experiments. The fluorescent immunosensor based on self-assembled multilayers has great potential for the rapid, sensitive detection of trace amounts of microcystin-(leucine–arginine) in real water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...