Guanine-based chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer biosensing platform for the specific assay of uracil-DNA glycosylase activity†
Abstract
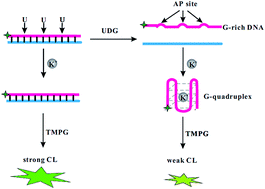
Assay of uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) activity is a crucial step for understanding some fundamental biochemical processes. Herein, we developed a simple and fast chemiluminescence (CL) method for the assay of UDG activity. In this method, one dsDNA probe containing fluorescein amidite-labeled G-rich ssDNA was used as a substrate for UDG. The dsDNA probe reacted with 3,4,5-trimethoxylphenylglyoxal to emit strong CL due to guanine-based chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer (CRET). The UDG-catalyzed uracil removal liberated G-rich ssDNA from the dsDNA substrate; then, in the presence of K+, G-rich ssDNA was converted to a G-quadruplex, which gives low CL emission. Therefore, using the CL response of the DNA probe as a signal indicator, UDG activity was determined in a simple process with high specificity, and a detection limit of 0.3 U mL−1 was achieved without any signal amplification. This simple and rapid methodology may have potential application in the UDG-related clinical diagnoses and functional studies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...