Microfluidic fabrication of polyethylene glycol microgel capsules with tailored properties for the delivery of biomolecules†
Abstract
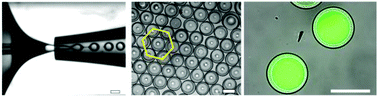
Microfluidic encapsulation platforms have great potential not only in pharmaceutical applications but also in the consumer products industry. Droplet-based microfluidics is increasingly used for the production of monodisperse polymer microcapsules for biomedical applications. In this work, a microfluidic technique is developed for the fabrication of monodisperse double emulsion droplets, where the shell is crosslinked into microgel capsules. A six-armed acrylated star-shaped poly(ethylene oxide-stat-propylene oxide) pre-polymer is used to form the microgel shell after a photo-initiated crosslinking reaction. The synthesized microgel capsules are hollow, enabling direct encapsulation of large amounts of multiple biomolecules with the inner aqueous phase completely engulfed inside the double emulsion droplets. The shell thickness and overall microgel sizes can be controlled via the flow rates. The morphology and size of the shells are characterized by cryo-SEM. The encapsulation and retention of 10 kDa FITC-dextran and its microgel degradation mediated release are monitored by fluorescence microscopy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators 2017


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...