3D printed structures for delivery of biomolecules and cells: tissue repair and regeneration
Abstract
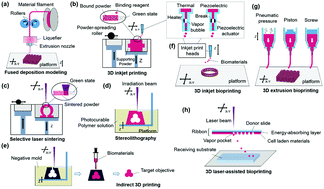
This paper reviews the current approaches to using 3D printed structures to deliver bioactive factors (e.g., cells and biomolecules) for tissue repair and regeneration. We discuss the benefits and critical points of potential scaffold materials and delivery strategies, particularly approaches that entail spatiotemporal variation in delivery. We also examine and critique advanced vascularization techniques, including delivery of angiogenesis factors and vascular cell sources. With further development of fabrication methods and functional materials, the 3D printed structures with embedded biomolecules and cells can be used as an effective therapeutic tool with controllable features for versatile drug delivery and tissue regeneration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...