Recent progress in layered transition metal carbides and/or nitrides (MXenes) and their composites: synthesis and applications†
Abstract
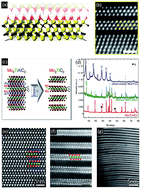
Since their inception in 2011, from the inaugural synthesis of multi-layered Ti3C2Tx by etching Ti3AlC2 with hydrofluoric acid (HF), novel routes with a myriad of reducing agents, etchants and intercalants have been explored and many new members have been added to the two-dimensional (2D) material constellation. Despite being endowed with the rare combination of good electronic conductivity and hydrophilicity, their inherent low capacities, for instance, temper their prospect for application for electrodes in energy storage systems. MXene-based composites, however, with a probable synergistic effect in agglomeration prevention, facilitating electronic conductivity, improving electrochemical stability, enhancing pseudocapacitance and minimizing the shortcomings of individual components, exceed the previously mentioned capacitance ceiling. In this review, we summarise the development and progress in the synthesis of various multi-layered carbides, carbonitrides and nitrides, and intercalants, as well as the subsequent processing in order to delaminate them into single- and/or few-layered and incorporate into MXene-based composites, focusing on their performance and application as transparent conductive films, environmental remediation, electromagnetic interference (EMI) absorption and shielding, electrocatalysts, Li-ion batteries (LIBs), supercapacitors and other electrochemical storage systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...