Introduction of an organic acid phase changing material into metal–organic frameworks and the study of its thermal properties†
Abstract
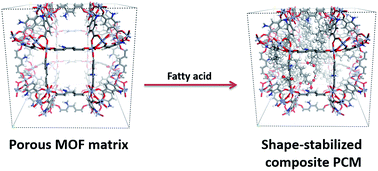
The design and synthesis of a shape-stabilized composite phase change material (PCM) is the most practical approach for addressing the leakage issue of phase change materials. This manuscript describes a facile solution impregnation method to access a novel type of shape-stabilized PCM employing metal–organic frameworks as the matrix. A fatty acid@metal–organic framework (MOF) composite PCM for low temperature heat storage has been developed for the first time. The metal–organic framework serves as an ideal host material for achieving a composite PCM taking advantage of its highly porous structure and tunable host–guest interactions. PXRD, FTIR, SEM, TGA, BET and DSC characterization studies have been conducted to reveal the structural and thermal properties of the newly achieved PCM composites. The results showed that one-step synthesized MIL-101-NH2 provided the most optimal thermal properties and the highest stearic acid mass percentage was achieved at 70 wt%, which corresponds to the highest loading and highest enthalpy in the literature for organic acid derived shape-stabilized PCMs. Furthermore, the thermal performance of the fatty acid@MOF composite PCM was maintained after 50 cycles, which indicates its great thermal stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...