Effects of molecular crowding and confinement on the spatial organization of a biopolymer
Abstract
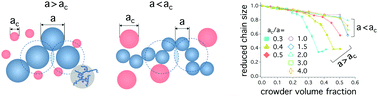
A chain molecule can be entropically collapsed in a crowded medium in a free or confined space. Here, we present a unified view of how molecular crowding collapses a flexible polymer in three distinct spaces: free, cylindrical, and (two-dimensional) slit-like. Despite their seeming disparities, a few general features characterize all these cases, even though the ϕc-dependence of chain compaction differs between the two cases: a > ac and a < ac, where ϕc is the volume fraction of crowders, a is the monomer size, and ac is the crowder size. For a > ac (applicable to a coarse-grained model of bacterial chromosomes), chain size depends on the ratio aϕc/ac, and “full” compaction occurs universally at aϕc/ac ≈ 1; for ac > a (relevant for protein folding), it is controlled by ϕc alone and crowding has a modest effect on chain size in a cellular environment (ϕc ≈ 0.3). Also for a typical parameter range of biological relevance, molecular crowding can be viewed as effectively reducing the solvent quality, independent of confinement.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...