A five-coordinate Mn(iv) intermediate in biological water oxidation: spectroscopic signature and a pivot mechanism for water binding†
Abstract
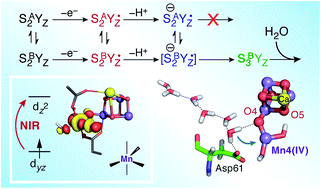
Among the four photo-driven transitions of the water-oxidizing tetramanganese–calcium cofactor of biological photosynthesis, the second-last step of the catalytic cycle, that is the S2 to S3 state transition, is the crucial step that poises the catalyst for the final O–O bond formation. This transition, whose intermediates are not yet fully understood, is a multi-step process that involves the redox-active tyrosine residue and includes oxidation and deprotonation of the catalytic cluster, as well as the binding of a water molecule. Spectroscopic data has the potential to shed light on the sequence of events that comprise this catalytic step, which still lacks a structural interpretation. In this work the S2–S3 state transition is studied and a key intermediate species is characterized: it contains a Mn3O4Ca cubane subunit linked to a five-coordinate Mn(IV) ion that adopts an approximately trigonal bipyramidal ligand field. It is shown using high-level density functional and multireference wave function calculations that this species accounts for the near-infrared absorption and electron paramagnetic resonance observations on metastable S2–S3 intermediates. The results confirm that deprotonation and Mn oxidation of the cofactor must precede the coordination of a water molecule, and lead to identification of a novel low-energy water binding mode that has important implications for the identity of the substrates in the mechanism of biological water oxidation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...