Identification and genotoxicity evaluation of two carbamate impurities in rasagiline
Abstract
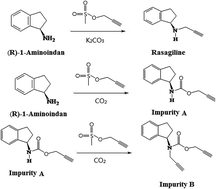
During the synthesis of a second-generation monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor rasagiline, two unknown impurities (impurity A and impurity B) were detected and isolated by preparative liquid chromatography. Based on mass spectroscopy and NMR, these two impurities were characterized as the by-products with a propargyl carbamate structure, whose generation was related to the carbon dioxide in the alkaline reaction solution. Because the carbamate structure has been highlighted as a class of potentially genotoxic impurities (GTIs), the genotoxicity of these two impurities was evaluated by the malformation test and the comet assay using zebrafish embryos. The results showed that the genotoxicity of impurity B was significant higher than that of rasagiline and other impurities. Thus, a HPLC-MS method was developed and validated for the determination of impurity B in rasagiline. The established method showed a good specificity, linearity, precision and accuracy. The detection limit of this method was 2.0 ppm with 0.1 mg ml−1 rasagiline mesylate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...