Hierarchically structured, well-dispersed Ti4+ cross-linked chitosan as an efficient and recyclable sponge-like adsorbent for anionic azo-dye removal†
Abstract
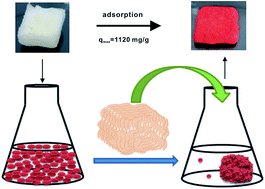
Porous macro- and hierarchically structured materials with desired morphologies and high adsorption capacities are of great interest because of their potential applications in realistic environmental pollutant treatment. In this study, sponge-like Ti4+ cross-linked chitosan (SL-TiCs) was synthesized using a chitosan solution and titanium metal salt as precursors. The as-prepared product was characterized via FE-SEM, HR-TEM, EDS, EMI, FT-IR and XPS. The results demonstrate that SL-TiCs is composed of multiple nano-layer twisted sheets and a high content of well-dispensed Ti4+ on its surface, which provide plenty channels for mass transfer and active sites for pollutant adsorption. The hierarchical structure of SL-TiCs exhibits a high adsorption capacity for Orange II with a fast adsorption rate and good recyclability. The adsorption performance can be described by the pseudo-second order and Langmuir isotherm models. The maximum adsorption capacity is 1120 mg g−1, which is much higher than that of many other adsorbents. It is speculated that the probable mechanisms involve ligand exchange (44.6%) between Cl− and dye–SO3− and electrostatic attraction (55.4%) between Ti–OH3+ and dye–SO3− anions in the adsorption process. This study implies that SL-TiCs can be a potential adsorbent for the adsorption and separation of anionic dyes from large volumes of industrial dye wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...