Functional block copolymer nanocarriers for anticancer drug delivery†
Abstract
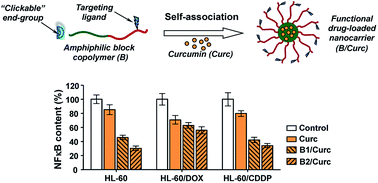
Polymer-based nanocarriers for anticancer drug delivery bearing “clickable”, biodegradable, pH-sensitive and subcellular targeting functions were designed and successfully obtained. Firstly, well-defined functional amphiphilic diblock copolymers were synthesized applying a multistep controlled polymerization and modification procedure. As a result, copolymers comprising alkyne-end functionalized biodegradable poly(D,L-lactide) and polycationic poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) blocks were obtained. The latter blocks were additionally functionalized with subcellular targeting triphenylphosphonium cations. The amphiphilic block copolymers self-associated in aqueous media into nanosized functional micelles that were able to incorporate the natural anticancer drug curcumin into their biodegradable cores. The in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of block copolymer micelles indicated a low intrinsic inhibitory potential on the proliferation of different human cell lines. More importantly, the drug-loaded nanocarriers demonstrated an obvious ability to induce apoptosis and exhibited more prominent inhibition of the NF-κB transcription factor in cancer cell lines and their drug-resistant analogues, as compared to the free drug. The obtained results are optimistic for potential application of the functional block copolymers in nanomedicine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...