Selenium and benzeneselenol interaction with Cu(111)†
Abstract
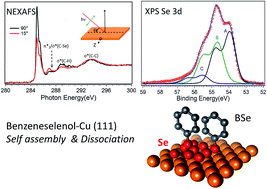
A study of selenium and benzeneselenol (BSe) interaction with a Cu(111) surface was performed, to investigate adsorption characteristics and molecular orientation. We report core level binding energies (CLBE) determined using high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and near edge adsorption fine structure (NEXAFS) measurements. The Se chemisorption study complements the work on molecules providing data on the CLBE's for the atomic case. Se adsorption was performed using immersion into a Na2Se solution and annealing in vacuum. Annealing results in the appearance of ordered structures in low energy electron diffraction (LEED) images. The fits of Se 3d XPS spectra show the existence of several components related to different adsorption configurations depending on annealing temperatures. Coadsorption with S was studied, which leads to changes in adsorption configurations. Annealing after simultaneous adsorption leads to progressive S elimination. In the case of BSe adsorption, XPS and NEXAFS spectra indicate Se–C bond scission, leading to the appearance of atomic Se. This is accompanied by the coadsorption of molecules. NEXAFS revealed a degree of dichroism, showing that the molecules are tilted at about 30° from the surface normal, assuming a homogeneous layer. The results show that the molecular layer is formed on a complex interface that could affect electron transfer properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...